The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond. Resonance of the Peptide Unit.
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
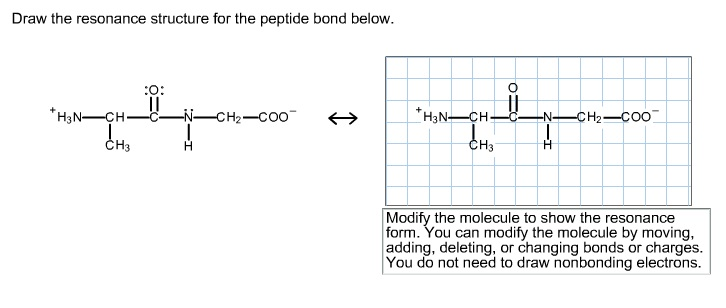
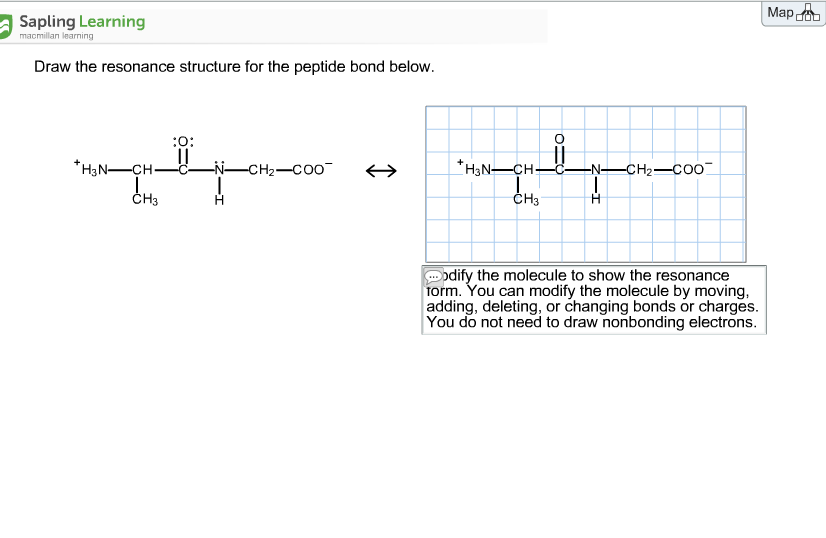
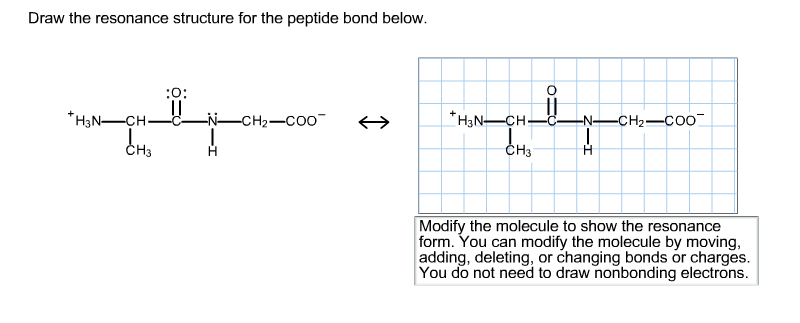
Modify the molecule to show the resonance form.

. Meanwhile the basic groups terminal amino group and R group of. The peptide bond has approximately 40 double-bond character. The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond Options is.
As a result it is rigid. Pauling and Corey showed that in small peptides six atoms associated with the peptide bond all lie in a plane. The formation of a peptide bond is what type of reaction.
The resonance structures that can be drawn for the peptide bond indicate that the peptide bond Options is. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond. Also shown are the individual dipole moments arrows associated with each bond.
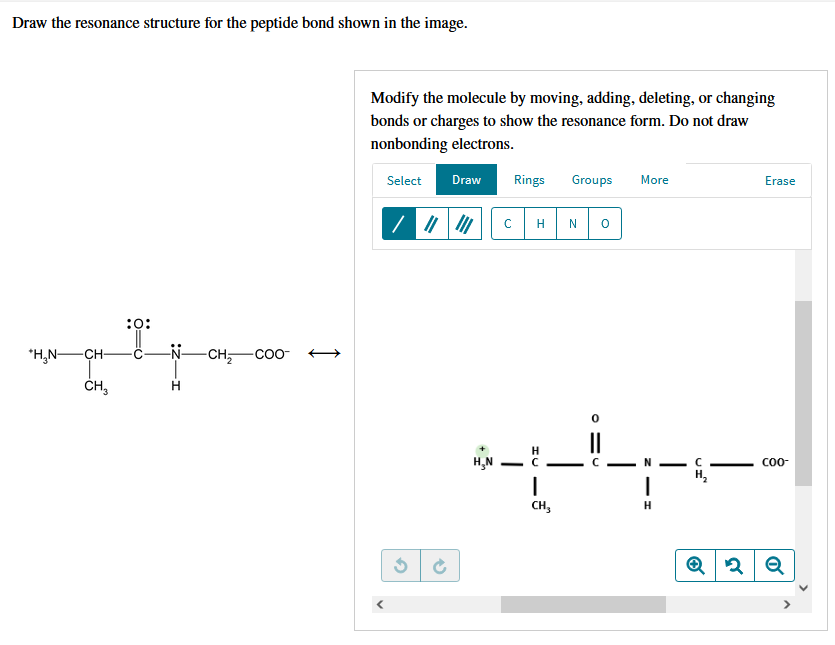
Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below. Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond. You do not need to draw nonbonding electrons.
Has partial double bond character 2. The amide structure has two resonance contributors. The resonance structure prevents rotation around the peptide bond.
The resonance structure is a significant factor in depicting the true electron distribution. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
Charges result in the peptide bond having a permanent dipole. This problem has been solved. The structure of the peptide KHNP at pH 7 is shown below.
Oh and H the bond Oh eight and H two. Draw a dipeptide of two amino acids in trans linkage side-chains can be shown as R and indicate which six atoms are part of the planar structure of the peptide bond. HaN CH CHz_COO HzN- CH- CHz- CoO CH.
Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen. Click on the structure below to switch the resonance forms of the peptide bond. The intermediate resonance structure imparts a partial double bond characteristic to the CN bond thereby prohibiting rotation.
Below draw the resonance structure of the peptide bond. Draw the formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids. The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures.
The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures. The dashed lines indicate the resonance of the peptide bond. This problem has been solved.
Select Draw Rings Groups More Erase. Who are the experts. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below.
The peptide bond would be right here. Modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges to show the resonance form. The coplanarity of the peptide bond denotes the resonance or partial sharing of two pairs of electrons between the amide nitrogen and carboxyl oxygen.
So theres air Die peptide and were asked to circle the peptide bond. Protein phosphorylation is an example of what. We discussed three secondary structure motifs.
View the full answer. CHz Modify the molecule to show the resonance form. HN-CHC_NCH-COO- Сн н C -.
The real structure of course is a weighted hybrid of these two structures. Backbone R3 C O H H H N C C R2 R1 O C O H H 118 120 122 121 123 123Å 152Å 145Å 133Å 116 N N C C H C peptide plane peptide plane R1. You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Thus the peptide unit is a planar rigid structure and rotation in the peptide backbone is restricted to the bonds involving the a carbon. Do not draw nonbonding electrons.
Draw the resonance structure of a peptide bond and explain why there is no rotation around the CN bond. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below. You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting or changing bonds or charges.
The amino acids are taken from the crystal structure of hemoglobin αVal 132 and αSer 133. This is a Most important question of gk exam. Both and 5.
Is stronger than an ordinary single bond 3is still not completely understood 4. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Each peptide bond is shown in a shaded box.
At pH 7 all of the acidic groups terminal carboxyl group and the R group of histidine are deprotonated. Who are the experts. The four atoms that are part of the peptide bond are shown as larger spacefilling models.
24 is asking us to draw the resident structures of the peptide bond so we can start by trying are a peptide bond. We review their content and use your feedback to. Resonance structure of peptide bond Peptide Bond A peptide bond is a covalent bond found in the primary structure of a protein.
The peptide bond has approximately 40 double-bond character. The structure at the right shows a peptide bond between the amino acids valine Val and serine Ser. Or changing bonds or charges_ You do.
Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond shown in the image. The atoms C H N O of the peptide bond lies in the same plane like the hydrogen atom of the amide group and the oxygen atom of the carboxyl group are trans to each other. The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids which is connected by the p.
You can modify the molecule by moving adding deleting. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. So our die peptide will be Oh double Bond.
Because the bond between the carbonyl carbon and the nitrogen has a partial double bond character rotation around this bond is restricted. Lets draw the structure of the die peptide glycerine and serene. Draw the resonance structure for the peptide bond below.
And then to get the residents structure we can move the electrons from this double bond up to the oxygen that we can move this lone pair from nation between the carbon and nitrogen. KHNP is also known as lysylhistidylasparagylproline where the lysine residue is the N-terminal and the proline residue is the C terminal. Therefore a reasonable resonance structure can be draw with a double bond linking the carbon and nitrogen and which result in a negative charge on the oxygen and a positive charge on the nitrogen.
4 pts See page 74 of the textbook.

Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com

Oneclass Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Below Modify The Molecule To Show The Re
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com
Solved Draw The Resonance Structure For The Peptide Bond Chegg Com

0 comments
Post a Comment